IV.4. Science, Technology, and Innovation
The 2040 Strategy requires robust support in terms of expertise, technology, innovation, and human talent to leverage the competitiveness of the traditional business, diversify energy sources, accelerate decarbonization, and implement the TESG agenda. This is why “Cutting-edge Expertise” is one of the drivers of the Company’s vision, and within this, the science, technology, and innovation (ST+I) strategy continues to evolve and is consistent with global trends in terms of technology and innovation, which materializes into the commitment to generate an incremental EBITDA of between 20 and 30 TRILLION USD by 2040, with the unification of the portfolio, joint planning with the business, and execution systems.
Declaring CT+I as the main lever for sustainable growth acknowledges the need to adapt, adopt, develop, and access, by means of global knowledge ecosystems and forms of science, technology, and innovation applied to the great challenges of the energy transition and climate change. In this order of ideas, the Ecopetrol Group established a link between strategic goals and technological challenges through clusters, which propose disruptive solutions to major obstacles using cutting-edge technology. These clusters are the guiding principles of the CT+I strategy. They steer and focus the efforts of the Ecopetrol Group and its Energy Human Tech ecosystem:
Ernesto Gutiérrez de Piñeres, Vice President of Science, Technology, and Innovation, is the leader of the CT+I strategy, materializing it into an evolving operating model to ensure flexibility, agility, strategic focus, and superior performance, by means of four (4) dimensions:
CT+I Planning: CT+I investment guidelines and portfolio planning.
Innovation and orchestration: scouting of solutions, maturation, and steering.
Execution depending on internal capabilities and technological maturity.
Marketing and technology transfer.
Furthermore, the CT+I strategy strives for: (i) productivity: agile, simple, compliant, and productive processes to focus people on activities that generate value, (ii) extension of capabilities: smart digital operations and infrastructures, and (iii) cybersecurity: secure and available digital operations. Consistent with this, the Vice Presidency is also made up of a cybersecurity and cyberdefense management unit.
CT+I Value in 2022
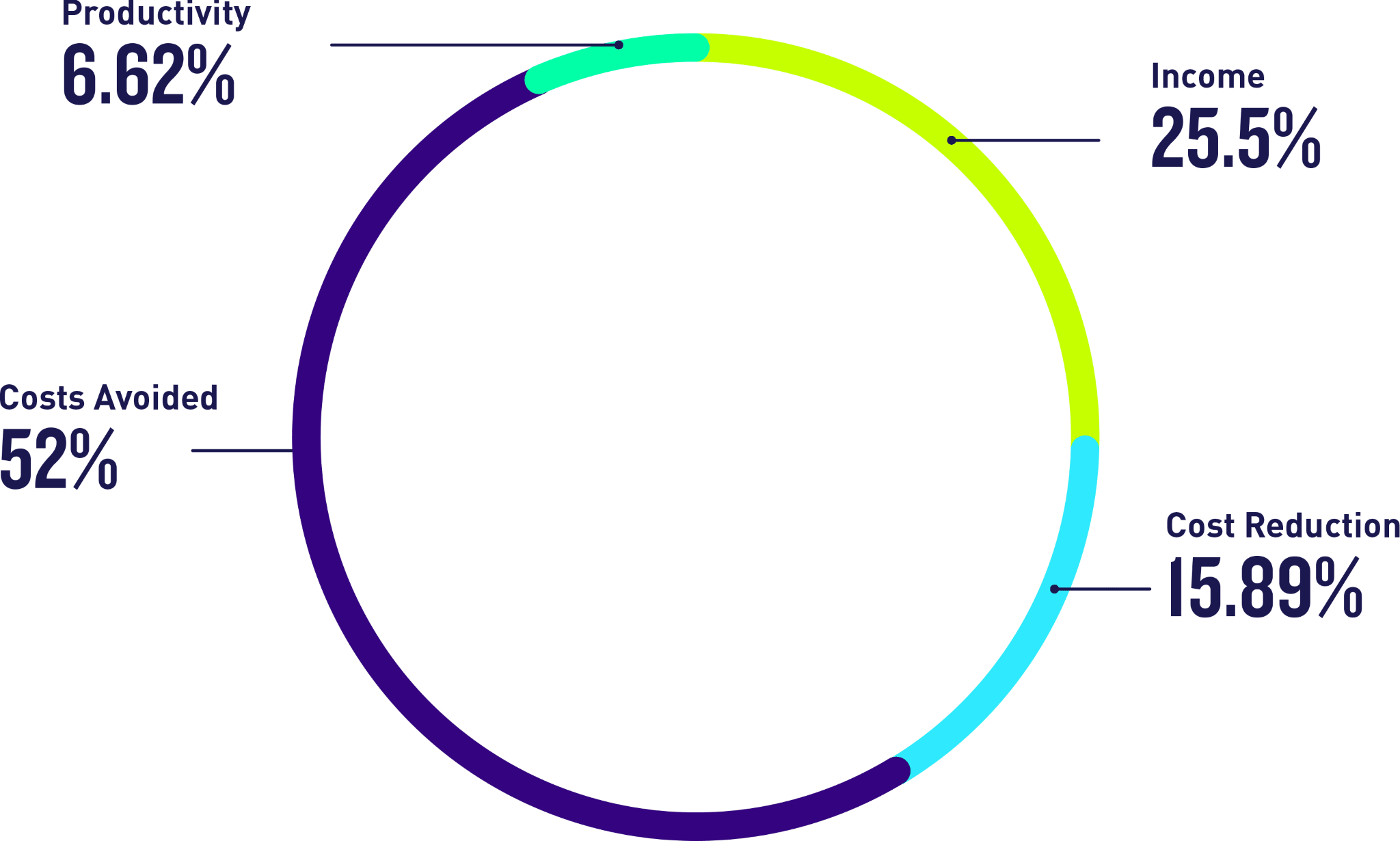
In 2022, the CT+I portfolio consisted of 201 projects in execution, generating certified benefits in the amount of 595.67 MUSD. 42% of these benefits are reflected in income, mainly from incremental production ~5.06 Mbbl, avoided deferrals, reduction of costs and expenses, reduction of CAPEX, and optimization of midstream inventories. The income from the licensing of technologies to third parties is also worth highlighting, with important technologies such as EGOs, which helps reduce the theft of fuels in hydrocarbon transportation infrastructure; Codilution, a system that injects LPG as a codiluent for crude, reducing the requirement for naphtha and other high-value inputs; and Jupiter Additive, which improves the mobility of heavy crude, thus reducing naphtha requirements in production operations; and the income generated from the provision of support and technological development services to Group companies and third parties.
The CT+I initiatives contributed to the operating efficiency, the generation of TESG value and the competitive advantage of the businesses, through the automation of processes and the implementation of cutting-edge technologies.
The digital agenda highlights the value deriving from the implementation of cutting-edge technologies to systematically scale up smart, safe, and sustainable products and processes for the Group. The implementation of the energy optimization project stands out, which generated benefits due to the reduced gas consumption in the operation of the Barrancabermeja and Cartagena refineries, and also contributed to the reduction of 14,578 tons of CO2eq emissions. Similarly, the implementation of the digital programmer in the operating supply chain contributed to maximizing the crude oil margin and reducing the cost of financing the stock.
With regard to the business technology agenda, the certified benefits are worth highlighting thanks to the performance of the FCC catalysts in the Barrancabermeja refinery, which allowed higher production and improved quality of valuable products (gasoline and diesel). The use of the Jupiter technology in the Chichimene field also led to higher revenues due to the mitigation of 1,673 Kbls of deferred production. With the implementation of the Codilution technology, the Group’s operating margin improved by optimizing dilution costs, substituting part of the imported naphtha for the dilution of Castilla, Chichimene, and CPO9 crudes, using LPG from the Apiay, Cusiana, and/or Cupiagua plants.
The CT+I strategy represents a value promise of 2.5 TRILLION USD in cumulative EBITDA between 2018 and 2023. To date, the value generated amounts to 2.5 TRILLION USD (100% of the promise), of which 1.86 TRILLION USD are certified and 638 MUSD are written off.
| Digital Transformation Investments | R+D+i investments and expenses | |
|---|---|---|
| 2019 | 51.70 | 33.6 |
| 2020 | 65.10 | 22.03 |
| 2021 | 53.30 | 41.41 |
| 2022 | 60.37 | 44.68 |
* Note: Includes only figures for R+D+i investments and expenses in business technology. The creation of the Vice Presidency of CT+i and the Innovation and Technology Center – ICP in 2022 consolidates and leads the execution of the digital transformation and business technology portfolio.
2022 CT+I Balance
Energy Transition

CCUS: development of the methodology, protected as a Copyright Registry for evaluating the effectiveness of Roca-Sello. This methodology is applicable to the evaluation of conventional prospects and is of great relevance in the evaluation of Roca-Sello for the geological storage of CO2, which was used successfully to analyze the pre-feasibility of CO2 storage in the Castilla, Chichimene, and Llanito fields (mugrosa formation).
A surface monitoring methodology for CO2 emissions was implemented using remote sensors, which established a recommended workflow to monitor vegetation anomalies due to the presence of CO2. The work was implemented in the Putumayo basin (San Gabriel block), and the methodology is scalable for the generation of the necessary baselines in the areas intended for CO2 geological storage projects.
High enthalpy geothermal areas: identification of geothermal potential in the Colombian subsoil, specifically in the deposits of Cordillera (P50: 152 MW) and the Llanos basin (P50: 59 MW), as well as the identification of technologies and possible strategic partners for development and use.
Together with the Vice Presidency of Low Emission Solutions, a request was filed with the Ministry of Mines and Energy (MME) for polygons under a transitory regime, geothermal exploration projects in areas located in Llanos (Manacacias-Almagros) and the Rubiales and Caño Sur fields. The corresponding exploratory permits were requested for these polygons, in order to conduct studies that contribute to the geological, geophysical, and geochemical understanding of the areas and their respective high enthalpy geothermal reservoir. Based on the MME’s response on exploratory polygons requested by Ecopetrol, high enthalpy geothermal projects in Llanos will focus on Rubiales and Caño Sur, where thermal gradients greater than 50°C/Km were identified.
A subsurface geological model of the Valle de Nereidas area was produced, including the discrete fracture network (DFN), in order to locate the best drilling prospects in this high enthalpy geothermal area.
1
Offshore power generation: the theoretical power generation potential of each source (marine/ocean currents, offshore wind, tidal, floating solar, thermal gradient, and saline gradient) in the Colombian maritime territory was determined, with offshore wind potential being the most prominent at present in the northern Caribbean region. A methodology based on SIG3 was similarly generated to identify unrestricted areas, coming from aspects such as underwater facilities, marine ecological conservation zones, fishing activities, among others. Finally, the best technologies applicable to Colombia for the generation of offshore renewable energy were appraised and selected, establishing their degree of technological advancement and adaptability to the conditions of the Colombian maritime territory, which is critical information to leverage the Ecopetrol Group’s energy and decarbonization transition plans.
2
Green hydrogen production pilot test: this took place between April and August at the Cartagena refinery, with a production of 775.53 kg of high-purity (99.997%) H2, which was incorporated into the refinery’s operation. The test validated the performance of the PEM technology (proton exchange membrane cells). This green hydrogen reduces CO2 emissions by 9.7 Kg for each kg of H2 generated, compared to gray hydrogen.
Decarbonization

1
Natural carbon sinks: carbon quantification and monitoring methods were formulated in five (5) strategic ecosystems (wetlands, rain forests, Andean forest, moorlands, and Caribbean mangroves) due to their decarbonization potential for the country.
2
The design of the spatial, environmental, and ecological data infrastructure began, together with Microsoft, with standards, procedures, and technological resources for the management of Nature-Based Solutions, including multiple technological tools for decision-making in decarbonization matters, management of environmental obligations, environmental incidents, and socio-environmental investment, which served as an innovative digital information management model for the Company and its Group, as well as for the territories and for global analyses.
3
A CT+I partnership between IDEAM, Fundación Natura, and ICP is working on a structure that generates value for the country by updating the national cartographic information on land cover to revitalize the processing, interpretation, and analysis of data on changes in coverage, and co-formulating the quantification and monitoring protocols for strategic ecosystems that expand the portfolio of decarbonization alternatives for Ecopetrol and its Group.
TESG and Circular Economy

The first versions of the water management platform, developed jointly with Accenture and AWS, were deployed focusing on the optimization of water catchment, use, and discharge processes at the Barrancabermeja refinery, in the conventional (Ocelot de Hocol field) and unconventional (Permian) upstream. This platform represents a key effort towards the goal of being a water neutral Company by 2045.
Technological and business model innovations were made in circularity and in the use of water as an Ecopetrol Group asset. In 2022, sustainable production was enabled using water and hydrocarbon separation, and domestic and industrial wastewater polishing technologies. Progress was similarly made in obtaining nanofertilizers and microbial consortia for agroforestry irrigation, enabling a new alternative for water evacuation and advancing in the implementation of the water neutrality strategy, by ensuring the reduction of catchment and discharges.
In terms of hydrocarbon circularity, technological developments were generated to allow the production of new materials from heavy refining bottoms such as Demex and PetCoque.
Progress was made together with Esenttia in the chemical recycling initiative, with the evaluation of two (2) pyrolysis oils from Spain and Brazil. This evaluation evinced that it is possible to obtain propylene yields of at least 10%. Also, plastic samples from the Manizales landfill (Colombia) were characterized.
Resilient Assets and Business Technology Services:

780,000 incremental barrels of oil added to the production goal with the use of:
- Enhanced recovery technologies: air injection, foam injection for steam recovery, and chemical injection for the conformance of water injection processes.
- Well stimulation technologies: Nano Water Wetter, NanoRPM, and EcoRPM.
Carbon-intensity was reduced by 55.4% in the cyclical steam injection process, and the energy efficiency of the process increased by 54.88% with the implementation of preformed foam technologies, which led to an incremental oil production of 12,000 barrels.
The injection wells in the Casabe field were optimized with the use of conformance and broken pipe sealing gels at high-concentration formulations, which recorded an incremental production of 28,000 barrels of oil.
The biostratigraphic support (identification of the target horizon using microfossil analysis) contributed to the successful drilling of the discovery well in the Uchuva – 1 discovery, by specifying the correct position in depth of the gas reservoir.
The implementation of the codilution technology in Cusiana reduced up to 63% in the use of conventional diluent (naphtha diluent) per barrel of LPG injected (1.7 BLS of conventional diluent / barrel of LPG injected).
1.7 MBLS of deferred production were mitigated thanks to the application of the Europa additive in two wells in the Suria field (T2 formation) and in areas of the Chichimene field where no diluent was available to transport production fluids from the clusters to Chichimene station.
Transformation of laboratories and pilot plants of the Innovation and Technology Center (ICP):
- Improvements were made to the Laboratory Management System in 2022 by ensuring good quality practices in compliance with the NTC ISO/IEC 17025 standard, thus increasing the quality and efficiency of the experimental activity by simplifying procedures and requirements.
- Progress was made in the technological transformation of the laboratories and the maintenance area of the ICP, in line with the implementation of digital information management tools and the automation of statistical analysis processes and the interpretation of results.
Industrial Revolution 5.0

The energy transition advanced with the implementation of the Visual Mesa digital tool, which allows real-time optimization of the power generation systems at the refineries using digital twins of the gas, steam, electricity, and water power systems. This increases process efficiency and reduces operating costs and CO2 emissions at the refineries. An emission reduction of more than 35,000 tons/year is expected by 2023.
A digital solution was designed and implemented to support the scheduling decisions of the crude supply chain by developing a genetic algorithm that simulates and optimizes crude flow scenarios from the well to the export or refining site.
ROMSS4, a system to manage inventories, movements, and balances, was implemented in the Cartagena and Barrancabermeja refineries, facilitating and expediting decision-making in volumetric processes with a direct impact on the refining margin.
In partnership with Accenture, Claro, and Microsoft, the first 5G pilot test for industrial use was conducted in maintenance operations at the Barrancabermeja refinery, with the use of secure devices for real-time remote assistance, which reduced three (3) days of maintenance and generated optimizations in the activity amounting to more than 1 MUSD.
In 2022, Campo D (digital field), a set of digital factories focused on developing products using agile frameworks, stood out in Accenture’s Business Agility measurement as top performer in agile maturity, exceeding the benchmark by 26 points when compared to more than 4,600 teams around the world, including Fortune 500 companies. The most relevant results were: (i) development of more than 700 accumulated digital products for the business, including robots, chatbots, analytical models, software developments, datamarts, integrations, and master data, (ii) 286,000 man-hours released, leading to a cumulative productivity of 606,000 man-hours, (iii) more than 5.3 million successful transactions, (iv) more than 200 robots operating, and ( v) more than 50 products for subsidiaries such as Esenttia and Cenit.
Ecosystems
An agreement was entered into with the State of Bavaria, Germany, to exchange knowledge in sustainable development models, energy transition, methodologies and best practices, and in leveraging technological developments. This agreement has allowed Ecopetrol to actively present its technological challenges to different German companies, in order to hear alternative innovative solutions from the different companies and seek potential paths of collaboration to solve these challenges.
The Company is working together with Finland to learn about their experience developing ecosystems thanks to the efforts deployed by their government. The main information exchanges for 2022 include the presentation of ECO3, a specific decarbonization and biogas ecosystem.
Ecopetrol has consolidated itself as the leading company in the development of technology in the country, with the highest number of patent applications and patents granted.
As of December 2022, Ecopetrol holds 124 valid patents, 16 of them granted in 2022 (13 in Colombia, 2 in Venezuela, and 1 in the United States).
Some of the benefits of these innovations include: (i) separation of fluids during the crude oil extraction process to start the treatment of the water produced in the well, (ii) use of nanotechnology to control microorganisms in production water and pipeline deterioration in the oil fields, (iii) cost reduction in the first phase of the crude production process, (iv) reduction of the carbon footprint, and (v) development of environmental studies in sea and ocean ecosystems using an underwater glider.
| Intellectual Property Registry | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Granted patents | 5 | 15 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 16 |
| Newly filed patent applications | 12 | 17 | 19 | 17 | 24 | 17 |
| Copyright registrations obtained | 39 | 25 | 41 | 46 | 31 | 37 |
Furthermore, as of December 2022, Ecopetrol registers seventeen (17) accumulated industrial secrets, seven (7) industrial designs, and (23) licensing contracts that monetize part of Ecopetrol’s technology portfolio.
Risks Associated with Intellectual Property and Controls
Ecopetrol has identified three (3) risks associated with intellectual property, for which it has established a series of controls whose effectiveness is periodically monitored by the Company.
Lack of technical rigor in the structuring of technology assessments and business cases for the commercial exploitation of solutions. To mitigate this risk, the business cases presented to the Business Opportunities Committee are approved upon being submitted to the expert judgment of the ICP managers and other members of the Committee.
Inadequate capture of the economic and strategic value of licensed technologies. To mitigate this risk, improvement actions are monitored, controlled, and incorporated into the marketing plans and licensing contracts for each of the licensed technologies by reviewing the commitments acquired.
Leakage or loss of highly classified technical-scientific information and failures in the implementation of intellectual property protection strategies for technological solutions developed by Ecopetrol. To avoid the materialization of this risk, the technological products developed are approved, with the definition of the intellectual property protection strategy and the complementary protection thereof in the Scientific Technical Committee of the ICP.
Innovation
- More than 100 challenges captured in all segments of the Ecopetrol Group.
- Roughly 350 startups contacted during the exploration phase.
- 24 challenges launched into national and international ecosystems.
- 21 pilots started and 14 pilots completed to date as a result of the open innovation process.
- More than 80 direct jobs created.
- Around 1.5 MUSD executed in the deployment of pilots.
Some of the outstanding results include:
- Drilling schedule, in order to reduce operating costs by optimizing the drilling schedule.
- Office Hotelling, which provides a solution for the optimization and assignment of jobs in the new normal.
- Remote monitoring, allowing an 80% reduction of CAPEX in the model and mitigating the risk of seizure and the likelihood affecting the integrity of the infrastructure.
- Prediction of occupational diseases, to warn of the risk of diseases, improve the work environment, and increase productivity. This initiative is implemented by the Ministry of Health of Colombia.
Econova
Proprietary brand for the Ecopetrol Group’s Science, Technology, and Innovation strategy
The new CT+I vision is built around the Science and Technology Campus – ICP in Piedecuesta (Santander). This technological development center has been leading industry research in the country for more than 35 years, with highly specialized talent and technological and scientific infrastructure, generating invaluable knowledge for the country.
The Econova Innovation and Orchestration Network seeks to consolidate an Energy Human Tech ecosystem focused on solving challenges and cross-cutting missions of the industry, through regional open innovation centers, as shown in the image below:
FIRST ENERGY HUMAN TECH ECOSYSTEM
At the service of the industry, the country, and latin america
1
Knowledge arising from great challenges and emerging echnological challenges.
2
Generation of technological solutions by means of the global business tissue
3
Permeate borders by orchestrating the CT+i ecosystem, generating creation, collaboration, and development with global impact, in the region and the territories and communities of Colombia.

The strategy currently contemplates the creation of five (5) interconnected regional nodes: Caribe, Antioquia, Meta, Bogotá, and Santander. The purpose of this ecosystem is to orchestrate knowledge and strengthen the country’s innovation network by connecting with external innovation laboratories and capacities.
The Innovation Center in the Caribbean was deployed in 2022, with the following remarkable achievements:
Agreements with the Caribbean Chamber of Commerce for the articulation of the ecosystem and the operation of the center, with the National Learning Service (SENA) operating the technopark and the Cartagena refinery operating the mobility park.
The incorporation of a virtual layer through the metaverse of the Innovation Center, which has been visited by close to 500 people, including Colombian businesspeople, government officials, and entrepreneurs, who have toured the green hydrogen generation system, the micro -LNG pilot, and the integrated water management platform, in order to disseminate awareness about these projects.
Within the framework of the International Mission of Wise Men, the Ministry of Science, Technology, and Innovation, the Ministry of Mines and Energy, and Ecopetrol entered into a third cooperation agreement aimed at scaling up manufacturing processes, constructing ecosystems and capacities for the energy transition, and strengthening regional innovation centers in pursuit of turning Colombia into a productive, sustainable, and equitable knowledge society. Ecopetrol contributed 10 million USD to this end and will focus on issues such as non-conventional energies, bioindustry, water circularity, and CCUS.